
Overall, 81 countries (42 per cent of all countries worldwide) have e-waste policy, legislation, or regulation in force. However, according to June 2023 data, the growth rate of countries implementing e-waste policy, legislation, or regulations is decelerating, and most ITU Member States still have no legal instrument in place governing e-waste management. To assist Member States in balancing their economic and social development with environmental management, ITU provides a programme dedicated to e-waste policy and regulatory development.
Through previous and ongoing projects and partnerships with key players including WEF, UNEP, GIZ, CST, DITRDCA and EU Africa RISE Facility, ITU has become a trusted implementer of projects which aim to improve the national regulatory framework for e-waste management.
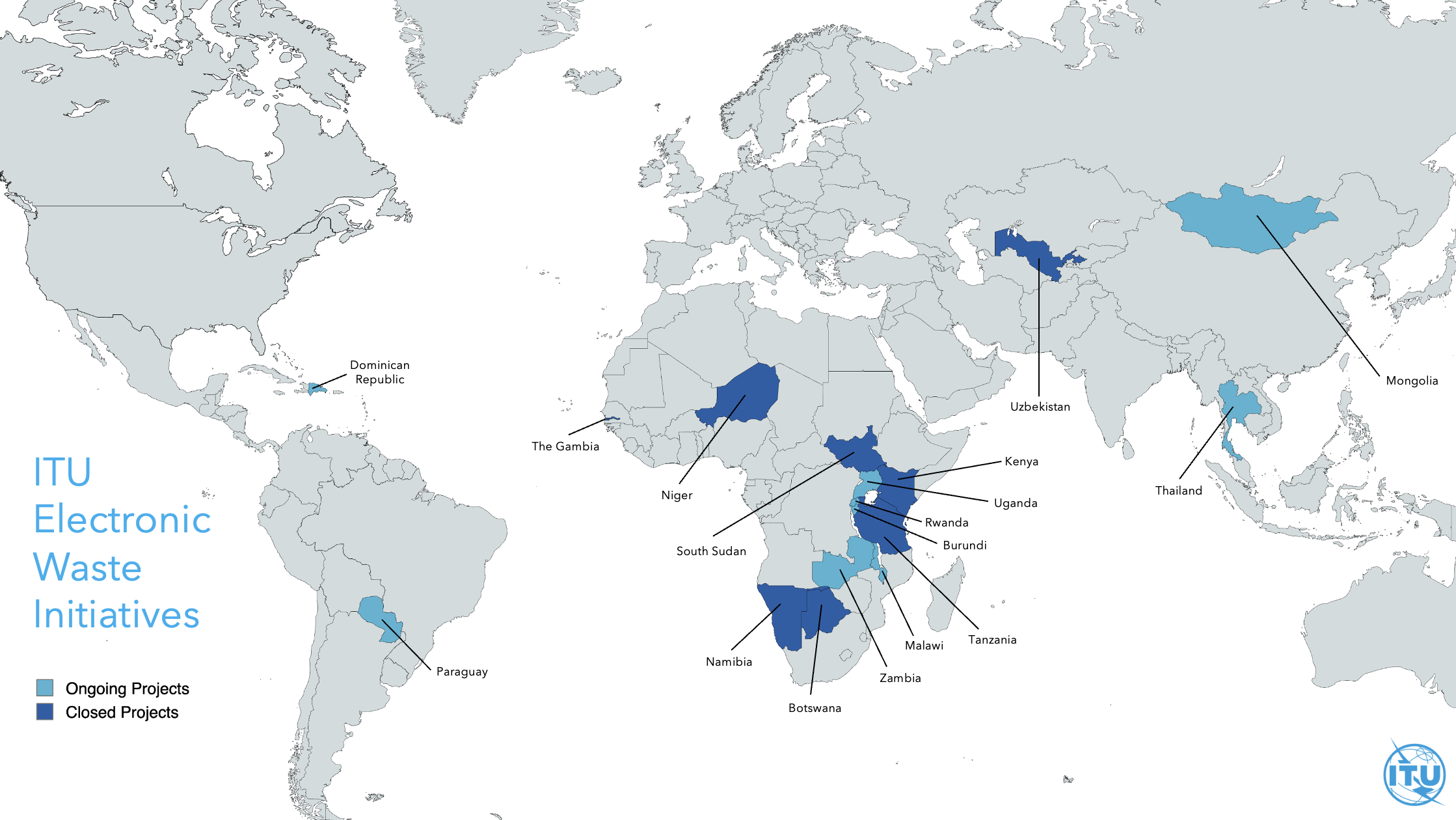
Disclaimer: The designations employed and the presentation of material on this map do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of ITU and of the Secretariat of ITU concerning the legal status of the country, territory, city or area or its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries.
Global Impact
Having an e-waste policy or legislation in place is a significant first step for a country towards creating a system of environmentally sound e-waste management, transitioning to a circular economy for electronics and increasing the amount of e-waste collected and recycled. The Global E-waste Monitor 2024 tells us that those countries with e-waste legislation in place have on average a collection rate of 25 per cent whereas the majority of those without legislation have a collection rate close to zero.
Countries Supported