|
|
|
Abstracts |
|
9:30 – 10:00 |
Opening Session: Welcome Remarks |
|
Chairman: Arthur Levin, Chief, Services Department, International Telecommunication Union - Telecommunication Standardization Bureau (ITU/TSB) |
|
Welcome address: Dr Awni Behnam, Commissioner General of the UN Pavilion |
|
10:00 – 11:30 |
Session 1: ICTs and the reduction of GHG emissions: Reducing the carbon footprint of the ICT sector (future networks, data centers, recycling) and using ICTs to reduce GHG emissions in other sectors (smart buildings, smart girds, dematerialization).
|
|
Moderator: Paolo Gemma, EU Senior Marketing Manager for Europe, Representative of Huawei Technologies, China and ITU-T Study Group 5 Rapporteur (Q17/5): |
|
Speakers: |
|
Arthur Levin, Chief, Services Department, International Telecommunication Union - Telecommunication Standardization Bureau (ITU/TSB):
ICTs as a tool to combat Climate Change: An overview |
Xia Zhang, Senior Engineer, China Academy of Telecommunications Research, MIIT: Reducing carbon from ICTs - Promote the universal power chargers for ICT devices
Presentation on the universal power adapter and charger solution for mobile phones and other ICT devices, reduce the e-waste, especially introduce the important new Recommendation ITU-T L.1000 (L.adapter) Universal power adapter and charger solution for mobile terminals and other ICT devices.
 |
|
Presenters: |
Raja Aida Binti Raja Shaharuddin, Student's Project/Seminar Coordinator, College of Science & Technology, UTM International Campus, Malaysia: Restructuring towards Green Computer Lab and Data Centre
The practice of just replacing older computers that are no longer useful
as it does not support the green computing approaches. Currently, a
variety of different features for newer green desktops, laptops,
servers, monitors and other computer hardware that have been produced
and introduce. The main advantages of most green computers are their
energy efficiencies. Most new computers are being designed to use less
power more efficiently but this does not mean that the computer
performance is slow. This is a move to make computers to perform more
efficiently. Powerful computers require more energy which inturn
generate greater amount of heat that adds to global warming. In this
context, popularizing green technology in terms of reducing house gas
emissions, waste and pollution towards the preservation of the
environment, may generally have a small impact in comparison to the
demand for computers. Green computer advocates properties such as the
use of non- hazardous materials and the elimination of using heavy
metals which are generally used in computer manufacturing. In addition,
greenery close to building further contributes to the importance of
bio-climatic functions that creates more favourable climatic conditions
for the building’s inhabitants and aids in reducing overheating in the
laboratory (or lab) environment, which ultimately preserves the health
of mankind. Therefore, in restructuring a green computer lab and data
centre , the structure of the building itself needs to be emphasized.
The aim of this paper is to present and discuss three major aspects in
restructuring green computer laboratory and data centre , among others,
are: (i) the use of solar energy within the lab and the type of
equipment used; (ii) the fixtures in the building such as air
ventilation, fixtures such as skylight and minimizing the use of air
conditioners and (iii) the use of recyclable materials. These efforts
could provide some solutions in promoting green computer laboratory and
data centre which may it be economically or ecologically, for the
betterment of mankind.
Keywords: Green computing, Green computer lab, Green computer,
Bio-climatic functions; Global warming |
Nakarmi Bikash, J. Sangirov,
M. Rakib Uddin, Y. H. Won, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Photonic Energy and Signal processing Lab, Daejeon, Republic of Korea:
Efficient Approach Towards Energy Minimized Optical Network
The rapid increase in Internet traffic is accelerating the demand for the higher traffic capacity in recent
years. This increase in traffic drives a continued growth of telecommunication infrastructure through
deploying of new technology with the transmission and switching equipment. The power drawn by IT
infrastructure is receiving significant attention as it is a key contributor to greenhouse gasses. However
the power drawn by the IT is comparatively lower, but growing rapidly which is a key environmental,
social and political issue. Various approaches have been taken in order to overcome these problems. One
approach towards it is so called “The electronics bottleneck” is to replace of electronics router which is
the main power consuming component by the optical router in which optical packets are buffered and
routed in optical domain. However this solution is an appealing one; still there are many questions
regarding the physical size of optical buffers and switches compared to electronics to be answered before
implementing it for the future growing network.
A number of research papers and surveys show that hybrid (Opto-Electronics) technology will be best
option for the future network considering the physical size, power required, internet traffic and others.
Numbers of experiments and analysis are carried out with the optical and electronics buffer technology
separately and few have discussed about the hybrid technology. However they are just limited to only
other parameters like capacity, packet drops, QoS but failed to consider the power consumed by the
hybrid technology which has been of growing interest in recent years.
Wavelength converter in the network has the potential impact on the power consumption. So our main
focus of research is to minimize the power consumed by the WCs and minimize the number of
wavelength converter. Previous research shows various methods of implementing the wavelength
converter using optical technology however the advancement made by the electronics technology made it
more feasible on implementing the WCs using OEO converter i.e. the hybrid technology. We found that
using the OEO converter for wavelength converter can significantly reduce the power consumption and
our implementation record it as a reduction up to 70%.
Another approach to minimize the power consumed by the wavelength converter is to minimize the
number of WCs in the network. To address this issue, we have taken the heuristic approach of traffic
grooming in optical network. We implement the idea of lambda run graph approach to minimize the
number of WCs and hence the power of the network considering other parameters draws the constant
power. The basic idea of lambda run graph approach is to bypass the node which has the same
wavelength. It is constructed with the number of available group of wavelength called lambda run to
represent the availabilities of wavelength converters, wavelength channels, and optical transceivers along
a physical route selected for routing a new connection request. The problem of dynamic wavelength
assignment that minimizes the number of wavelength conversions can be obtained through this algorithm
and hence the cost and power of the optical network can be minimized.
With the proposed idea, by combining these two approaches we can reduce the power consumption up
to 80% than the traditional approaches of using all optical wavelength converters and routing algorithm.
Hence the proposed algorithm and modification on the all optical wavelength converter has a potential to
save the power consumed by today’s internet technology which can help to build the Greener IT and a
Greener city. |
Yang Yang, Professor, Shanghai Research Center for Wireless Communications (WiCO),
China: Cooperative Wireless Networks for Better Green Services
During the last two decades, mobile communication systems (such as GSM, GPRS and 3G networks), wireless broadcasting networks, wireless local area networks (WLAN or WiFi), and wireless sensor networks have been successfully developed and widely deployed through different technological routes for providing a variety of communication services and applications. While making tremendous contributions to social progress and economic growth, these heterogeneous wireless networks consume a lot of energy in achieving overlapped service coverages, and at the same time generate strong electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radiation pollution, especially in big cities with high building density and user population. Very timely, this talk aims to address these important issues by proposing a cross-network cooperation mechanism to effectively share network resources and infrastructures, and then adaptively control and match multi-network energy distribution characteristics according to actual user/service requirements in different geographic areas. Some key research challenges will be highlighted and discussed in detail. Initial analytical results show the proposed approach can significantly improve multi-network energy efficiency, reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emission, EMI and radiation pollution, and support sustainable development of new services and applications across multiple cooperative wireless networks. |
Daniel Mauricio Amaya Madrid, Universidad Distrital Francisco José de Caldas, Bogotá, Colombia:
Wireless Networks for trade community
In order to have an excellent economy in the Andean region Colombia has to implement technology in their industry at the moment is that we help students to implementing systems that help disadvantaged communities of our cities provide services for them are inaccessible because their purchasing power, such as deploying a network to which people in a specific region can access for free to offer products and services, this implementation should be done involving the state and the private sector to fund the project, taking note that after having implemented and operating a network of trade in the town can expand the network at the Internet, so that so users who originally only bought and sold staples such as clothing, shoes or food, have more products at your fingertips with just one click.
To do this you must implement not only a node with their respective teams as routers and antennas; if not also have people willing to train the community to manage the platform and can themselves performs maintenance on the equipment.
From the academy as students would implement the node and also would empower community also have to implement all possible applications that are within our reach as VoIP, applications to serve through the Bluetooth technology in mobile phones, also use equipment such as VeriSign company "offers prepaid service PrePayIN improved trade and settlement services themselves and billing services and next-generation OSS."
Another service that we are deploying software to the allocation of appointments in the community hospitals at this time, many hospitals in Colombia which we still Another service we can implement are software for the allocation of appointments in the community hospitals at this time, many hospitals in Colombia which we still allocate appointments where patients have to go to hospital in the morning and is given a tab, the idea would be to implement a software in which accessing from home or in an internet cafe near her to ask for the appointment and what can be done at any time, in addition to having this software is easier for doctors having a database with medical records of their patients.
Keywords - disadvantaged communities, applications, routers.
|
|
11:45 – 13:15 |
Session 2: The role of universities in building the Smart Cities of the Future: Research and Development, pilot projects, e-learning, providing wired and wireless services to citizens, e-commerce, online entertainment, sensors.
|
|
Moderator: Mercè Griera i Fisa, European Commission, Information Society and Media Directorate-General, ICT for Sustainable Growth Unit |
|
Speakers: |
|
"European funding opportunities for Research, Development and Deployment of Smart Cities projects": Mercé Griera i Fisa |
|
Presenters: |
Labonnah F. Rahman, M. R. Alam, Mohd. Marufuzzaman, M.B.I. Reaz and M.A. Mohd. Ali,
Dept. of Electrical, Electronic & Systems Engineering, Universiti Kebangsaan,
Malaysia: Smart Tracking: Usage of IPv6 in RFID system for
global mobility
The concept of internet is changing from the “network of computers” to the “network of things”. To recognize or sense anything a universal identification number is required. Currently, Barcode and RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) systems are being used for object identification which suffers from limited address space and local mobility. In this project, IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6) address will be used in RFID system which will provide a universal identification number to the objects with seamless global mobility. Instead of proprietary expensive RFID reader, the system will adopt Wireless Network Card which will be benefited by well defined IEEE 802.11 protocol. The EPC (Electronic Product Code) of conventional RFID tag will be used as MAC (Media Access Control) address in RFID-IPv6 transponder. This EPC will be mapped to IPv6 address utilizing auto configuration mechanism where 64 bit EPC will take place the EUI-64 portion of IPv6 address. As a result of this research, applications employing RFID system related to e-government, e-health, and e-commerce will be benefitted with significant cost reduction, physical location detection and globally unique address facility. Hazardous materials management under e-government systems will be able to maintain in a cost effective way without using the traditional RFID reader, physicians and healthcare professionals will be benefitted to automatically identify patient’s physical location in e-health sector. Moreover, supply chain management systems within e-commerce will discover and communicate with the product manufacturer by using globally unique address to boost up dealing time and turnover. Hence, using IPv6 in RFID transponder will be a unique solution for Information and Communication Technology (ICT) and smart society to the extent that telecommunication and the Internet have. |
Daniele Trinchero, Riccardo Stefanelli and Luca Cisoni, , iXEM Labs - DELEN, Politecnico di Torino, Italy; Abdullah Kadri and Adnan Abu-Dayya, QU Wireless Innovations Center (QUWIC), Qatar; Tamer Khattab, and Mazen Hasna, Qatar University, Qatar: Wireless sensors as an efficient way to improve sustainability in water management by a significant reduction of water wasting
Introduction
This paper presents an ICT solution to overcome the problem of water
dispersion in water distribution networks. Leakage prevention and breaks
identification in water distribution networks are fundamental for an
adequate use of natural resources. Nowadays, all over the world, water
wasting along the distribution path reaches untenable percentages (up to
80 % in some regions). Since the pipes are buried within the terrain,
typically only relevant breaks are considered for restorations:
excavations are very expensive and consequently the costs to identify
the position of the leakage or just the position of the pipe itself are
too high [1].
To address this problem, and simplify the leakage identification
process, the authors have designed a wireless network system making use
of mobile wireless sensors able to detect breaks and reveal unknown
tracks and monitor the pressure spectrum of the fluid flowing in the
pipe. The sensors transmit the acquired data from the terrain to the
surface by use of a wireless connection. On the surface ground there are
stations that receive the signal, process it, and communicate with a
central unit where necessary intelligent signal processing techniques
are
used to detect leakage sources.
Compared to other leakage detection solutions already available in the
market (such as: Ground penetrating radar (GPR), pure acoustic
techniques and tracer gases), the proposed technique appears very
efficient and much more inexpensive than the previous ones.
Description of the system
The proposed new solution is based on the use of a mobile wireless
sensor capabable of detecting breaks and revealing unknown tracks, by
monitoring the pressure spectrum of the fluid flowing in the pipe and
the relative speed within the fluid. The sensor transmits the
sensed data via a wireless channel, hence it does not require a physical
connection to the surface. The sensor gives an accurate detection of the
leakage location and it allows an easy and repeatable identification of
the track.
The application of the wireless concept to the water leakage detection
field allows the realization of mobile sensors able to flow together
with the fluid removing the constraint that characterizes the
traditional inspection techniques: the necessity of a wire between the
sensor and the surface. In particular, the sensor has been realized by
means of acoustic techniques, which are the most efficient in terms of
leakage identification, but also strongly limited in terms of distance
of application. Thanks to the mobility, the application range has been
extended significantly.
The proposed sensor is realized by means of a hydrophone that makes an
analysis of the fluid pressure within the pipe, which is further used to
recognize pipe damages or leakages, according to well known methods
reported in the literature [2]. The data collected by the hydrophone is
processed electronically, digitalized, stored on a flash memory and
transmitted to the ground surface, thanks to a dedicated antenna design
that allows wireless transmissions primarily out of the water and then
within the ground. The on-board antenna and microwave circuit is
designed by an innovative optimization process that takes into account
the water and the pipe itself as they were antenna components. The
wireless transmission is realized by means of a radio working between
200 MHz and 2500 MHz and compatible either with the IEEE 802.11 or the
IEEE 802.15 standards. Thanks to the implementation of such components,
the power consumption is kept within very low values and the survey can
be extended over long ranges (at least 5 kilometers). The sensor is
waterproofed and isolated from the water, thanks to a dedicated
manufacturing process. The system design involves the minimization of
the power consumption, thanks to a dedicated transmission protocol and
the pre-processing of the data on-board that optimize the amount of data
to be transmitted. The proposed new solution is based on the use of very
low cost wireless technology: in this way the final product is cheap, as
a mobile phone of average cost can be.
Results
Some prototypes are being realized and tested in real environments,
introducing the sensors within pipes located at different depths in the
ground. Experimental data show excellent performance and optimum
reliability.
Bibliography
[1] C. Lallana and N. Thyssen. Water use efficiency (in cities):
leakage. Environmental Indicator Fact Sheet, European Environment
Agency, 2003.
[2] Hunaidi O., Wing C., Acoustical Characteristics of Leak Signals in
Plastic Water Distribution Pipes, Journal of Applied Acoustic, 1998. |
Basile Spyropoulos, Medical Instrumentation Technology Dept., Faculty of Engineering, Technological Education Institute (TEI), Greece:
Smart Health Care in the city of the future: Patient treatment
at home and medical data exchange in the emerging networked society
1. INTRODUCTION
The modern Hospital emerged gradually and successively, during a very long historical evolution, from a religious philanthropy Institution to the contemporary managed care Establishment. The civil structure, the social demands, and the individual performance were always and are still reflected, on the Hospital, throughout the centuries. Therefore, the 21st Century Hospital will provide a radically different professional activity environment and a quite different professional-patient interaction modus; it will increasingly encourage Telemedicine supported home-care, because of the increase of mean life expectancy and the ongoing Hospital cost explosion. Its mission will be completed by a network of various associated Institutions, providing care rather closer to home-care, than to that of the traditional hospital-care.
Adapting Medical and Managerial Decision Making in the modern home-care environment is a cardinal prerequisite, in order to ensure, first, an economically sustainable development of the aging population health-care, second, the rehabilitation services required for impaired persons, and finally, the psychosomatic support necessary, during the next decades. Thus, a strategic question emerges that is how home-care will be medically supervised and financially reimbursed.
The presentation, by taking into account our own Research and Development experience, attempts to describe the contemporary technological trends in home-care, focusing on patient Diagnosis, Monitoring and Treatment at home and Medical Data Exchange, in the expanding networked urban and rural areas.
2. BIOMEDICAL TECHNOLOGY TRENDS
We argue that a qualitatively new “mobile” home-care is presently emerging out of the combined employment of, first, the modern wireless mobile telephony and equipment networks, second, the contemporary digital entertainment electronics, and third, the commercially available high quality and low cost computer hardware and software. This new mobile home-care allows us for to be optimistic about the reduction of patients’ unnecessary hospitalization in the near future, as well as, the dramatic reduction of the home-care cost. The miniaturization of equipment, and the falling prices trend that could be developed, by the opening of Biomedical Technology to the huge market of potential home-care equipment and material consumers, if combined with a “smart” home environment, will result in periodical, individually adapted, preventive Medical examinations at home, and, consequently, a decreasing number of patients in Hospital Wards and in Emergency Departments.
Wireless vital signal monitoring and critical functions support, among high-risk patients, suffering from chronic cardiovascular, respiratory etc. diseases, combined with point of care in vitro Diagnostic testing, and supported by sophisticated portable, laptop or even PDA sized Ultrasound/Doppler equipment, allow for the creation of affordable quasi Intensive Care conditions, at home.
3. CONTINUITY OF CARE AND MEDICAL DATA EXCHANGE
We argue that supporting the Continuity of Care at home demands, first, a typical Continuity of Care Record (CCR) adapted to support also the creation of a h-care plan, and second, a Prototype Ontology, based upon the Health Level Seven (HL7) Clinical Document Architecture (CDA), serving as basis for the development of Semantically Annotated Web-Services for the exchange and retrieval of home-care information.
The home-care plan module should support the creation of a structured subset of data, containing the diagnostic, monitoring, treatment, and nursing activities that should be employed, during the post-discharge home-care period, based upon a Classification of Diseases (e.g. ICD-10), a Diagnosis Related Groups (e.g. AR-DRGs), and a Nursing Interventions Classification (e.g. CCC) system. The proper representation of the concepts of these documents, in terms of ontology, ensures systems’ interoperability, and allows for the creation of semantically annotated Web Services, exceeding the problems of, both, incompatible formats in messages, and that of the use of diverse vocabularies.
5. CONCLUSIONS
Although, there is still a multifaceted set of problems, to be further investigated and deeper researched, there is enough evidence that the flexible hardware design and the adaptable data-exchange mechanisms presently available constitute already a useful and standard-compliant tool, for contemporary home-care.
|
|
14:15 – 15:45 |
Session 3: Cars and Intelligent Transport Systems: Using ICTs to green the transport industry; C2C communications, better traffic management, smart fuels, privacy.
|
|
Moderator:
|
|
Speakers:
|
Paolo Rosa, Head, Workshops & Promotion Division, International
Telecommunication Union – Telecommunication Standardization Bureau
(ITU/TSB): ITU Fully-Networked Car initiative
The periodical ITU-T Fully Networked Car workshops are in a unique position to
engage with that part of industry all too often missing from the ITS (Intelligent
Transport Systems) discussion: the motor industry itself. This presentation will
provide an overview on the ITU-T standardization related activities in this field
where convergentce of ICTs equipment, speech recognition, signalling, information
car and power industry can tremendously contribute to improve the life in future cities.
|
|
Presenters: |
Phan
Thanh Hoa and Takahiko Yamada, Ritsumeikan
University, Japan: An integrated mobile network supporting urban
activities
In future, mobile multimedia network will contribute to the
support of social activities more than the current cellular networks. Such
a network can link social activities efficient for a better life by keeping
on-line connections between not only normal mobile users but vehicular
users in further due to its ability of offering high data packet transfer. For
example in the modern transportation systems, in one hand, flexible
traffic light control can be achieved based on the gathered notification
from each car. On the other hand, the network can ask automobile the
optimized speed to pass the crossing section based on the estimation of
forward signaling periods. Interactive communication between network
and public bus will allow periodic arrival of buses at stops while
controlling the drive of buses.
The mobile multimedia network can be a measure of a life safety. The
mobile multimedia network is the measure of not only the intelligent
transport guiding-system but also always-provide of advanced
multimedia information. For example, if distance cameras are torched to
the before- or on-criminal act, moving picture are reported and stored.
This will contribute to the prevention of criminals.
Moreover, the mobile network should be a support of communications
in disaster. Some of base stations should provide back-up battery. And
some of radio resources for users in ordinary operation are turned to be
used for channels between base stations in case of disruption of
terrestrial network.
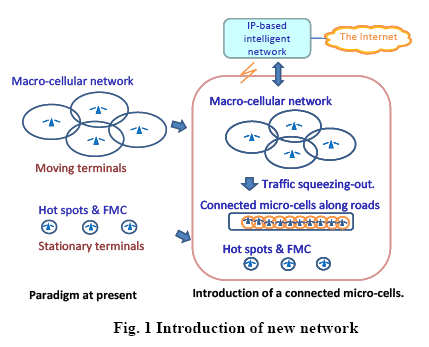
To meet some of advanced services stated above, the mobile multimedia
network with the fundamental structure from connected micro-cells along
roads as shown in Fig. 1 will become an essential network. It has been
designed to support mobile multimedia communications of fast-moving
terminals on the roads. Stationary terminals, otherwise, are assigned to hot
spots or FMC (Fixed Mobile Convergence). Communication traffic of
moving terminals on main streets is served by the connected micro-cells.
Therefore, the Macro-cellular network only handles the traffic of back
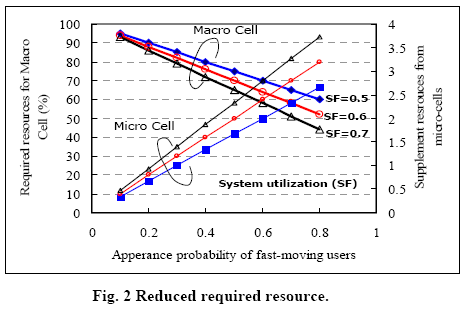
streets. As a result, the connected micro-cells system can help to reduce
the required radio resources in Macro-cell system as shown in Fig. 2.
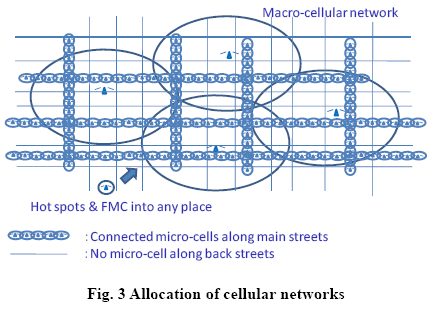
Three types of cellular network are allocated together in the metropolitan
area as shown in Fig. 3. Those three types of cellular networks can be
integrated to a ubiquitous network for each user. Mobile terminals should
be provided the soft-defined radio function to allow network-to-network
vertical handover. To accommodate a large number of access points for the
micro-cells, PON (Passive Optical Network) which is already used for
FTTH (Fiber-To-The Home) connection between many high-speed
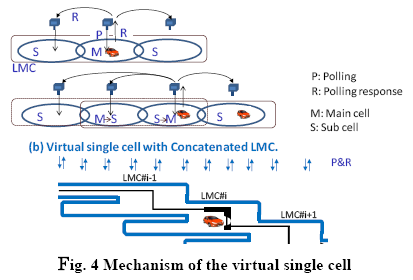
internet terminals can be a choice. In the connected micro-cells, a virtual
single cell is configured based on the mechanism shown in Fig. 4. Virtual
single cell operated by connection of concatenated LMC (Logical Macro
Cell) that groups adjacent cells in a multicast group to create a continuous
transmission environment for fast moving-terminal though parallel polling
process.
This paper aims to present and discusses the performance of how the
connected micro-cells network can offer high-speed packet transfer to
fast-moving terminal through the virtual single cell and parallel polling process that the primary contention-based known as a
fundamental procedure to support for wireless packet-based network but fail for mobility support.
|
Subin Shen, Professor, Vice-Director,
Institute of Information Network Technology, Nanjing Univeristy of Posts
& Telecommunications, China: Transport system
Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS) can provide functions of vehicle locating and navigating, traffic
monitoring, traffic jam warning, traffic accident warning, and public traffic scheduling. Global Position
System (GPS) is now used to locate vehicles. GPS and digital maps are used to navigate the vehicles.
Sensor, snapshot, and video analysis are used to monitor the traffic. There is no practical way to automatic
warn the traffic jams and traffic accidents. Since the Internet has no spatial semantics, it is impossible to
integrate all the isolated sub-systems of ITS. So it is difficult to realize the traffic-sensible navigation.
This presentation proposes a Spatial Semantic-enabled Next Generation Network (SS-NGN), which
is based on Internet Protocol (IP) extended with spatial semantics. By SS-NGN, the spatial information
sensed in the Physical layer can be used through IP in spatial computing in Application layer, and spatial
semantic-enabled computing can be performed directly in Application layer to satisfy the requirements of
ITS applications.
This proposal involves the spatial attribute definitions of network nodes, the spatial coordinate
reference in network systems, the adjustment mechanism between the spatial references of Physical
system and network system, protocols of access to spatial coordinate reference in network system,
navigating algorithms in spatial coordinate reference, deployment model of ITS based on SS-NGN, and
issues of international standards associated with SS-NGN.
SS-NGN can associate the spatial information of Physical layer through the IP layer with spatial
computing of Application layer of Internet. So the SS-NGN based ITS can inherit the scalability and
simplicity of Internet to make it easy to be deployed widely in the world.
The SS-NGN can make use of the network nodes deployed along the roads to establish
road-oriented spatial reference system which is consistent with physical space. The spatial attributes of
network nodes can be defined associated with spatial reference systems. The deployment of SS-NGN
overlaying the all roads of a city based on wired and wireless network can replace the GPS to establish a
simplified ITS within the city. This SS-NGN based ITS can integrate traffic monitoring and vehicle
navigating to provide traffic-sensible navigation. So it can mitigate traffic jams, make full use of roads and
reduce the carbon emission.
|
Sed Saad, Researcher, Waseda University and Senior Strategy,
Consultant, Telecoms & Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS):
Global perspectives of Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS)
Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS) has been designed in Japan as an effort to advance and apply ICT to
transport within a national Telecommunication Policy. This effort has been adopted as well in Korea. Such
perspective has differ from the US and EU which have a more conventional ITS approach, as Transport
Policy. Recently, based on new type of Academia-Government global partnership, MIT, in alliance with
Singapore, is following such telecom approach to ITS in order to duplicate worldwide the outcome to urban
areas.
Abu Dhabi, on the other hand, initiates a new approach on ITS, the” zero-carbon society (2015)” for green
next-generation transportation aiming to a green smart city with an ambitious pilot project, Masdar City, to be
fully operational by 2015. Japan also started to advocate such vision through NEDO/METI (Ministry) with a
similar project “Energy ITS” with a less ambitious vision, the “low-carbon society (2050)”
Beside Government and Academia, Industry is also looking to implement such next-generation transportation,
especially Nissan which adopted global strategy and new type of partnership with Governments, based on the
exclusive concept of electric vehicle. Nissan, aiming to become the leader for Electric Vehicle (EV) among car
makers, tackle as well the synergy of the two concepts –EV and ICT/ITS- to present the first examples of “
smart green cars”.
The aim of this paper is (1) to review different initiatives on a global level involving Academia, Government
and Industry (2) to unify such initiatives within an original framework and (3) to propose some
recommendations to support the vision of future sustainable green smart cities enabled by ICT
1-Different relevant initiatives and perspectives
| |
ACADEMIA |
GOVERNMENT |
INDUSTRY |
Areas |
| USA |
MIT |
|
|
Smart Cars |
| Singapore |
MIT |
Singapore |
|
ICT |
| Singapore |
|
Singapore |
MHI |
ITS |
| Japan |
Waseda |
Japan |
Nissan |
ITS |
| Japan |
|
Global Government |
Nissan-Renault |
EV-ICT |
| Emirates |
MIST-MIT |
Abu Dhabi |
|
Smart City |
| Emirates |
|
Abu Dhabi |
MHI |
Transport |
| |
|
|
|
|
2-Convergence of different initiatives under the motto “One World One UN”
Projects learning from each other
3-Recommendations for future sustainable green smart cities enabled by ICT
Need for new type of partnership models as well as new business models
|
Oscar Armando Contreras
and Yuly Jazmin Oviedo Melo, Universidad Distrital
Francisco José de Caldas, Bogotá, Colombia: Diagnosis of Pollution from vehicles: Meet the level of contamination of
your vehicle and learn how to reduce
Vehicular congestion contributes 53% of air pollution in Bogota, this city environment is still below international standards, Since the limit sets the level of concentration of material clean items (PM10) in 50.00 ug/m3 and in 2008 was recorded in Bogotá a concentration of 67.00 ug/m3, 17 points above the international boundary, although it should be noted that compared to 2007 fell by 4 points this concentration in the air. This concentration of PM10 in the air is the cause of 20% of respiratory diseases according to a study conducted by the District Health Secretariat and the Ministry of Environment in 2006.
Colombian law requiring all vehicles certified Gases, which is issued once a year, but in this time interval is not reliable as the vehicle is kept in top shape to reduce air pollution In today's market there are companies that provide services to owners in their vehicles as voice services, addressing road safety (vehicle location in case of theft), sudden changes of speed, all this using GPRS technology, in this same way is viable to install electronic sensors on the vehicle to check the levels of contamination of this, sensors for measuring CO2 levels would be located in the exhaust of the automobile and other sensors to be taking other values such as engine oil levels, recording time since last maintenance, etc. With these data, a diagnosis would be made through a web platform, indicating the driver's action to be taken to reduce levels of air pollution. Although currently there are modern cars that run on electricity is not available to everyone and this solution can be installed in conventional vehicles.
The technologies exist for different uses for commercial level, so it is important that meets the legislative role of governments to protect the environment and thus implemented through laws such as mandatory as this.
|
|
16:00 – 17:30 |
Session 4: Climate Change: Key issues for the green cities of the future: using ICTs to improve social conditions, e-government and e-health, promoting safe environments and identifying new strategies to adapt to and mitigate climate change.
|
|
Moderator: Arthur Levin, Chief, Services Department, International Telecommunication Union - Telecommunication Standardization Bureau (ITU/TSB)
|
|
Speakers: |
|
Presenters: |
D.M. Totev, P.Chakalisa, and D.Mapolelo, e-Government Researach Group, University of Botswana, Gaborone:
The Green Developing World or How the developing world becomes
developed
After the Copenhagen World Summit on Climate Change one might get an impression there is an unbridged division between Developed and Developing economies. At a closer look however, the differences are more politically rather than economically based. In reality the Developing countries could even benefit from the climate predicament, because, on one hand, they are not repeating the macroeconomic mistakes of the Developed world and, on the other hand, new low carbon industries could solve most of their socio-economic problem and increase their world significance.
It sound like a fantasy, but this paper tries to prove that it is quite possible such things to happen without the necessity of billions of investment. The major economic areas which could contribute to the success of the proposed transformation are:
- Transport industry
- Information Technology (IT) industry and Education
- Green industry
- Research and Development
Transport industry should be considered in broader terms as a system with the following main subsystems:
- National fleet
- Transport infrastructure
- Fuel supply and gas emission monitoring
- Maintenance and spares
The last subsystem provides a technological link with IT industry and Education.
The national fleet of Developing economies, as a norm, is made up of older models without any limit on their exhaust gas emissions. Thus, the very first task is to create a database of the individual vehicle emissions at a national level. Such an exercise could provide temporarily employment, mainly for young people, e.g. school leavers, university/college graduates. The necessary equipment is a standalone computer and a gas monitoring module installed on the computer. The same equipment could be re-used later on when it comes to fuel supply and gas emission monitoring
The total cost is about €700-800 per system. It will take not more than a year to prepare and submit a report to the relevant Government office on gas emissions at national level. At this point the Government has enough information to start negotiations with car manufacturers to trade the potential reduction of CO2 and other gases, if the old models are replaced by new ones. Obviously, such a Government scheme is a win-win approach to all parties concerned and could be supported by IMF as well. In addition sorted scrap out of the dismantled old vehicles could be offered in the form of pre-processed row materials, i.e. a new light industry is set-up and more job opportunities secured. The experience of Japan in this respect could be very useful. The corner stone of the Government scheme is a package of a few brand models only, plus infrastructure shares. The idea is that road quality is directly linked to gas emissions and maintenance cost and a bigger quota of vehicles could reduce their cost. The limit of a few models could contribute to improved maintenance as well, consequently further reduction of gas emissions, and bigger participation of world automotive industry in infrastructure projects.
At the same time, university departments, technical colleges and vocational centres could start training professionals to maintain and develop the most sensitive part of modern vehicles – the Engine Control Unit (ECU) – with respect to gas emissions. The learning process could be based on Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) which does not require big additional investment, e.g. component 16F84A costs less than 50 cents apiece and the programming unit is about €40 (demo is available).
Since the proposed Government scheme is not compulsory, other brand models could be found on the market, but their gas emissions should be checked every time they are re-fuelled. In case their emissions are out of range, the price of fuel is changed accordingly, stimulating the use of eco friendly vehicles only. But this is a new fuel supply industry closely linked to the green policy of Government.
The social and economic importance of Green industry is obvious and it could contribute further to the development of CO2 trading of the Government.
A visionary Government could invest in research and development projects as well, e.g. to develop a better engine with less emissions. Typical example is Variable Compression Ratio (VCR) engine developed by SAAB and other inventors of the Developing world. Such cooperative work could be the beginning of a new greener automotive industry.
In this way after 10-15 years a developing economy could join the club of the Developed world utilising the pressing necessity for alleviating the negative impact of climate change.
|
Heiler Yesid Ledezma Leudo and Heicer Enrique Ledezma Leudo, Researchers, Foundation of the Pacífic for the Advance of the Science and the Technology - FUPACTECNO, Bogota,Colombia:
Web territorial domains '.xx': Powerful tools of ICTs to offset GHG's emissions
It is known that the big extensions of vegetation generate big
quantities of breathable oxygen (O2). So that the vegetation is necessary
to get a reasonable balance between the Oxygen and the Greenhouse
gases (GHG), which are the principal causers of the climatic change,
and therefore of the global warming. In this scene (stage), it is
indispensable for the survival of the human species and all the species
that live (inhabit) the planet, that the concentrations of oxygen (O2) are
kept in the highest of the balance. Nevertheless, it seems that the
current transformations take place to a major pace that the previous
ones to the industrial age. UNESCO has catalogued a great list of sites
(places) worldwide as natural and cultural patrimonies [1]. In the world
context it is known that the major percentage of developing countries are
in Africa [2] and Latin America and the Carib [3]. If we center in the
natural patrimonies as axis (axle) of the subject matter of the present
text, in the list published by UNESCO [4], [5], it is evident that the sum of
natural patrimonies of Africa, Latin America and the Carib is of 68, and
exceeds for much the sum of natural patrimonies of continents with
major concentration of countries developed as the sum of Asia and
Oceania (they add 48), and North America and Europe (they add 56).
The Bio-geographical Choco [6, 7] is a natural neo-tropical corridor that
initiates its limits from the north up to the south like that: From Darién's
province to the east of Panama, crossing for the whole Colombian west
up to the northwest of the Ecuador and it ends in the north end of Peru.
Its great platform possesses: Coral mantles, mountains full of wild life,
immense rivers, humedales and tidelands bordered of exotic vegetation
with swamps, which they make bio-diverse to the Bio-geographical
Choco, a natural exchequer that the international community should help
to preserve. But this conservation will not come automatically. It is
necessary to give to it an impulse. This impulse would have been
extremely difficult some decades before because of the lack of access to
the Information and Communications Technologies (ICT) largely of the
world population. But though still (yet) today coverage is absent and is
necessary to extend the percentage of penetration in many countries,
the percentages (indexes) of penetration worldwide are encouraging in
the medium and long term [8], which converts the ICT into a potential
and powerful tool for to create conscience for the world population about
the need to preserve his natural patrimonies, for example in Colombia for
Bio-geographical Choco, which possesses big territories protected as
natural world patrimonies [9]. In the present, the only way that the
governments have of getting a lawful content in the web pages, is across
the web 'territorial domains', that is to say, the pages that at the end of its
web address they include for example: '.co ' for Colombia, '.br ' for Brazil,
'.pe ' for Peru, and more. These ' territorial domains' possess the
particularity of which to acquire them (unlike the web pages that do not
possess them) it is necessary that the institution that tries to obtain it is
due registered in the state competent organism (organisation), which
demand certain fundamental requirements to acquire such web territorial
domains. The authors of the present document propose to the ITU a
small web slogan (button) environmentalist against GHG (Green image)
to standardize it across procedure, regulations, standards, publications,
agreements, conferences, congresses, and more. To promote
mechanisms of pressure directed to the governments worldwide for:
- To determine that one of the fundamental requirements to
obtain web territorial domains in every country is that the web
page contains at least a link notably visibly (preferably in the
headline of the web page) with the small web slogan (button)
environmentalist which carries to serious and respectable
web pages of organisms (organisations) environmentalists
throughout the world accepted that they promote the world
creation of conscience for conservation of the natural
patrimonies of the country and decrease of GHG's generating
elements.

Green image. Web slogan (button) proposed by the authors.
This way, the exponential growth of the networks (nets) of information
would stimulate the growth of the environmental creation of conscience
worldwide, for example, the web pages of social networks (nets),
seekers, and blogs would stimulate that growth obligatorily.
This would represent a great advance in Colombia and all the world. Of
this way, the Information and Communications Technologies (ICT) are
the simplest form in order that the Colombian government and the
international governments would help to offset the global warming with
the Bio-geographical Choco in Colombia and the natural patrimony in
the world.
[1] http://whc.unesco.org/en/list/
[2]
http://www.uianet.org/documents/adhesion/Lista_paises_desarrollo.pdf
[3]
http://www.uv.es/~psudnord/Beques/Residencia/Anexo2Listado%20paises.pdf
[4] http://whc.unesco.org/en/list/
[5] http://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Patrimonio_de_la_Humanidad
[6] http://www.amatea.org/choco.php
[7] http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WKH2nqy0EO8
[8] http://www.itu.int/net/itunews/issues/2010/01/10-es.aspx
[9] http://whc.unesco.org/en/list/711
|
|
17:30 – 18:00 |
Presentation of Awards and Conclusions |
Sponsorship Opportunities
Sponsorship packages are available. We look for sponsors (platinum, gold, silver) to organize various activities, including a $10.000 prize fund for the three best papers. For other details please see the event web site here or contact
tsbworkshops[at]itu.int .
Catering Services
|
|
|



